Clip studio paint не работает трансформация
Обновлено: 04.07.2024
Free Transform in Clip Studio Paint is very simple. With it, you can scale your image, rotate it, flip your selection horizontally or vertically and even distort it a bit! I don’t use it for very complex actions, but I still use the Free Transform mode a lot! Constantly I need to make small selections of my drawings so resize them or rotate them to a position where it makes more sense.
How can you Free Transform a selection in Clip Studio Paint? Simply go to ‘Edit -> Transform -> Free Transform or press ‘Ctrl+T’ on your keyboard. You’re now ready to make any change you need to make!
You might notice though, that once you enter this mode, some options and settings will appear and there’s more to Free Transform than it looks at first glance. Let’s see in detail all the ways you can resize, rotate and even distort your images and how!
Here’s How You Free Transform In Clip Studio Paint
I use Free Transform a lot while working. Mostly very simple things. Resizing the whole work or just parts of it, flipping things around and very rarely distorting things a bit.
It is a very common tool, very useful and easy to use! You can access it by either selecting the layer or layers you want to transform or make a selection of a specific part of your drawing. After that, you can go to ‘Edit -> Transform -> Free Transform’. Alternatively, you can use the shortcut by pressing ‘Ctrl+T’.

Scaling and Rotating
Once you enter in Free Transform mode, a frame will appear around your selection. The points around this frame can be used to scale up and down your drawing or to rotate it. Just hover the mouse above these and then click and move.
When you’re able to rotate the selection a curved arrow with two ends will appear. To resize, it shows a straight arrow. Very simple and similar to other drawing software!
Careful with resizing though! If you’re using raster layers, you’ll lose quality as you scale things. For example, if you’re trying to scale it up, you’ll notice the selection will start to look fuzzy and distorted. If it’s a very small resize of the selection, it won’t be noticeable, but if you’re doing so, better use vector layers, so you won’t lose any quality in your drawings!
I always use vector layers for my line art so that I can resize them if I ever need to. That way I’m never worried about having to redo my lines because they lost quality.
Skew And Distort
Even though Clip Studio doesn’t have a clear option to skew and distort a selection in the menu, you can do it while in Free Transform mode.
Simply hover the mouse over the points that show around the frame. Press ‘Ctrl’ and a small white arrow will appear. Click the Left Button of your mouse while pressing Ctrl and you can now skew and distort your image! You can do this with either of the points and move everything around as you wish.
Free Transform Menu
Now, when you enter in Free Transform mode, you’ll notice a new tab to the left. This tab has a few options that you can use. For example, let’s say you need to rotate the selection you just made.

There are different ways to rotate. What I mean by this is that you can choose where the center of your rotation will be. It can be in the center of the drawing, top left, top right and so on. Depending on what you choose, the rotation will behave differently.
You can also select the scale ratio you want and even type in the rotation angle you need! At the top bar of the Free Transform window, there are also some useful buttons.
The first one will reset the transformations you made. The two that follow serve to flip your selection and then you can confirm or cancel the transformation.
If you end up doing something you don’t want to, let’s say you scaled the drawing up but decided it was too much, you can hit Ctrl+Z to undo your last move. You don’t need to cancel the whole transformation.
This is very useful because sometimes we’ve done quite a few changes and then misclick something by accident. If we cancel the transformation, it will cancel everything we did so far and now we have to repeat everything all over. Instead, just go one or more steps back with the ‘Undo’ shortcut and you’re good!
When you’re done with your changes, select the confirmation button on the tab to your left or simply press ‘Enter’. Your selection is now transformed!
Sometimes Clip Studio might take some time applying the changes you’ve made. Don’t worry though, most of the time it will pull through it. This happens because the selection you’ve made is very big and the software takes a bit more time to process it!
How To Flip Your Selection In Clip Studio Paint
There are different ways to flip your work or selection in Clip Studio. You can do it through Free Transform. Simple press ‘Ctrl+T’ and then you have two buttons on the Free Transform tab: one will flip the selection horizontally, the second vertically. Choose the one you want and when you’re done, press enter.
You can also go to ‘Edit -> Rotate/Invert Canvas -> Flip Horizontal or Flip Vertical’ to flip the whole canvas. Notice that you have other options in here as well, such as rotate by 90 degrees, 180 degrees, etc. You can do these simple rotations through this menu as well!

I want to take the time here to give a very quick tip: If you’re in Free Transform mode and want to rotate your selection by 90 degrees, press ‘Shift+LeftMouseButton’ and move the mouse around. This will rotate your drawing from 90 to 90 degrees, perfectly!
Flipping the whole canvas or a simple selection is very useful, especially if you’re drawing the human figure. While working, we flip our work to be sure the proportions are right and that everything makes sense, even seeing it from a different perspective
Scale The Horizontal And Vertical Ratio In Free Transform
As I mentioned before you can scale your selection by controlling its horizontal and vertical ratio on the Free Transform menu.
This means that instead of scaling using the frame around the selection, you can use these two bars. The first bar is signaled with a ‘W’, when moving the bar around you’ll notice that the width size is changing. The second, marked with an ‘H’ scales the height of the selection.
Personally, I feel it’s very weird to scale something using these bars. I prefer to have more control over it by moving my selection around. But, as always, everyone has their own preferences and both ways work!
Notice the option right below these bars. You can enable the ‘Keep ratio of the original image’ and now, if you scale the width of the image, the height will scale accordingly. This way you’ll avoid any kind of distortion in your selection!

If you have this option enabled and decide to use your mouse on the selection to scale it, the same will happen, maintaining the original ratio of the image. If you have the ‘Keep ratio of the original image’ disabled, you can also press ‘Shift+LeftButtonMouse’ when resizing and it has the same effect!
Frequently Asked Questions
Can you liquify in Clip Studio Paint? No. Currently, there is no tool or option to liquify in Clip Studio Paint, but you can do a similar process by using the Mesh Transformation option which I cover here (LINK!)
How do you rotate the canvas in Clip Studio Paint? As mentioned above you can go to ‘Edit -> Rotate/Invert canvas’ and choose one of the options. Alternatively, you can also use the rotate tool by pressing ‘R’ on your keyboard and rotate the canvas at will!











Transform
Selecting items from [Edit] menu > [Transform] with a layer selected, moves or transforms the selected layer.
Mode types
The Mode types listed under [Edit] menu > [Transform] are as follows.
Scales up/down or rotates the image. For details, see " Scale/Rotate " .
Scales up/down or rotates the image. For details, see " Scaling Up/Scaling Down " .
Rotates the image. For details, see " Rotate " .
Freely transforms the image. For details, see " Free Transform " .
Distorts the image. Dragging the corner handles of the bounding box moves the image in the direction of the the guide lines. Dragging the middle point handles of the bouding box, moves that line parallel to the other side of the guide line. For details, see " Distort " .
Skews the image. Dragging the handles moves the whole side of the image in the direction of the the guide lines. For details, see " Skew " .
Skews the image. Dragging any of the corner handles will move the opposite corner handle into the opposite direction. For details, see " Perspective " .
Flips the image horizontally. For details, see " Flip Horizontal " .
Flips the image vertically. For details, see " Flip Vertical " .
Mesh Transformation [PRO/EX]
Allows you to create guides and handles by dividing a selected area with a lattice to transform an image by portions by dragging the corresponding lattice point. For details, see " Mesh Transformation [PRO/EX] " .
Transform image
This section describes how to transform images in a variety of ways.
· For details on how to use [Flip Horizontal], see " Flip Horizontal " .
· For details on how to use [Flip Vertical], see " Flip Vertical " .
· For details on how to use [Mesh Transformation], see " Mesh Transformation [PRO/EX] " .
1 First select a layer on the [Layer] palette.

· Selecting multiple layers transforms all of the selected layers.
· To change the Layer Mask only, you must unlink the Layer and the Layer Mask. For details, see " Link Mask to Layer " .
· To change the Ruler only, you must unlink the Layer and the Ruler. For details, see " Link Ruler to Layer " .
2 Using the selection tool, create a selection.
· If there is no selection area, the entire drawn area of the selected layer will be the target of the transformation.
· Only selections on Raster layers, Vector layers, Layer Masks and Selection layers can be transformed.
3 Select the method of transformation from the [Edit] menu > [Transform]. In this example, [Free Transform] is selected.
4 Drag either the bounding box guide lines or handles to transform the image.
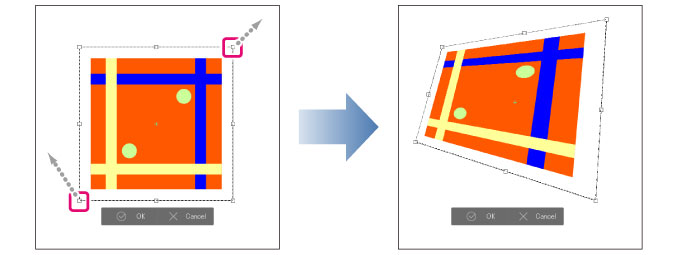
5 Click [Confirm] on the launcher below the bounding box to apply the transformation.
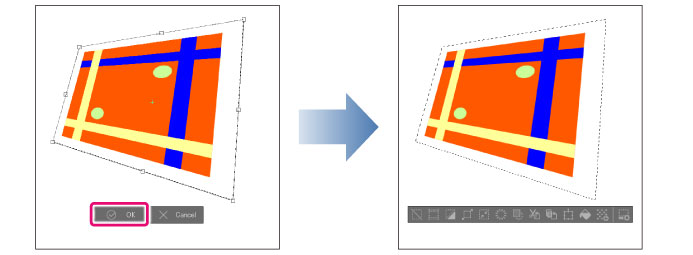
· You can double-click inside the bounding box to confirm the transformation.
· Pressing Enter also applies the transformation.
· Press Esc to cancel the transformation.
· If the [Transform launcher] does not appear, select [View] > [Object Launcher].
Using handles and palettes to transform
Selecting items from [Edit] menu > [Transform] shows the handles and guide lines allowing you to adjust them.
You can also adjust transformation values and the transformation mode from the [Tool Property] Palette.
For details on how to use [Mesh Transformation], see " Mesh Transformation [PRO/EX] " .
Using the handles to transform
Dragging a handle allows you to transform the image. The directions the handles can move depends on the transformation mode. For deatils on how to use, see " Mode types " .
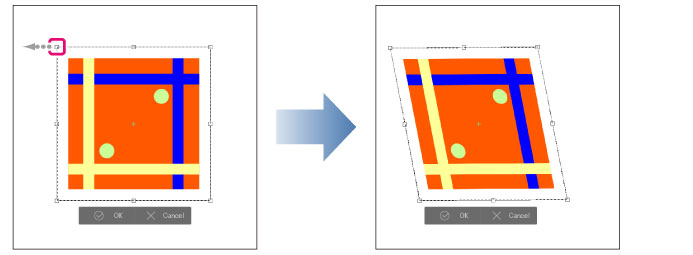
Move image
Click on the inside of the bounding box and drag to move the image.
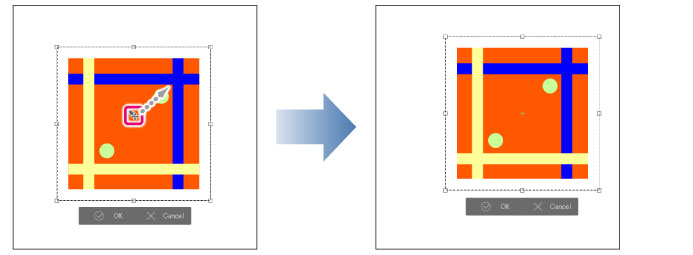
Hold down Shift while dragging the drawing area or bounding box to move the image horizontally, vertically, or along a 45-degree diagonal angle.
Rotate image
Drag outside the bounding box to rotate the image around the center (+) point.
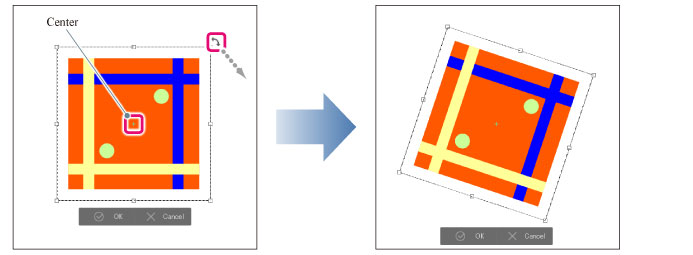
· Hold down Shift while dragging to rotate in increments of 45 degrees.
· Dragging the center moves the center of rotation. Change the center point’s position from the [Tool Property] palette’s [Center of rotation].
· Hold down Shift while dragging the center point to move the center point horizontally, vertically, or along a 45-degree diagonal angle.
· Hold down Alt while clicking the canvas to move the center point to wherever you click.
· You cannot rotate the image while using [Scale] from [Edit] > [Transform]. To rotate an image either select [Rotation angle] from the [Tool Property] Palette or a transformation option from [Mode]. For details on how to change this, see " Changing the Mode " .
Adjusting transformations with the Tool property palette
You can the image scale ratio and angle while transforming from the [Tool Property] Palette.
Changing the Mode
[Mode] on the [Tool Property] palette allows you to change the transformation method.

Tool property palette settings
When transforming, the following operations can be performed from the [Tool Property] palette.
· If the transformation is recorded in an auto action, [Auto action settings] will be shown in the [Tool Property] palette. For details, see “Transformation settings” in the Clip Studio Paint Tool Setting Guide .
· For details on how to use [Mesh Transformation], see " Mesh Transformation [PRO/EX] " .
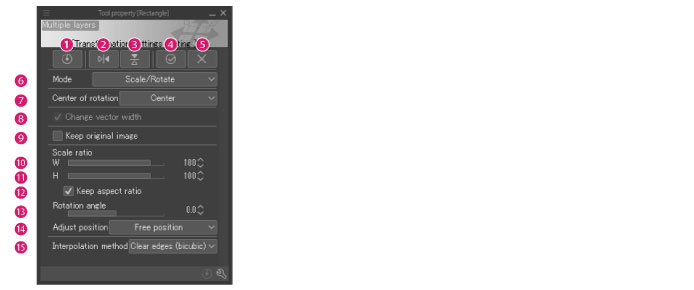
(1) Reset transformation
Restores the image being edited to its pre-transformation state.
(2) Flip horizontal
Reverses the image horizontally around the center.
(3) Flip vertical
Reverses the image vertically around the center.
Commits the transformation.
(5) Cancel
Cancels the transform.
(6) Mode
This setting changes the transformation mode. You can select from [Scale/Rotate], [Scale], [Rotate], [Free Transform], [Distort], [Skew] or [Perspective].
(7) Center of rotation
Sets the center of rotation for the image.
You can select from [Center], [Top left], [Top right], [Bottom right], [Bottom left], [Top], [Left], [Right], [Bottom] and [Free position].
(8) Change vector width [PRO/EX]
Turning this on allows you to scale the line width of a Vector layer, a Balloon layer or a Frame Border folder.
(9) Keep original image
When turned on, the original image can be kept when moving or transforming.
Selecting the next layer repeats the transformation on the duplicated layer. The original image is left on another layer.
· Image material layer
· Stream line layer
· Saturated line layer
(10) Scale ratio (Horizontal)
Specifies the horizontal width of an imported image as a percentage of the original image (%).
(11) Scale ratio (Vertical)
Specifies the vertical width of an imported image as a percentage of the original image (%).
(12) Keep aspect ratio
When this is on, the image will keep its original aspect ratio (proportions) when scaling up or down. Use the handles to keep aspect ratio of original image when scaling.
(13) Rotation angle
Specifies the image rotation angle with respect to the horizontal position.
(14) Adjust position
Allows you to adjust the size of an image being transformed automatically. The size is specified by the size of the bounding box.
The size of image’s bounding box can be adjusted within the size of the Canvas.
The size of image’s bounding box can be adjusted within the size of the Bleed border.
The size of image’s bounding box can be adjusted within the size of the Cropped border.
The size of image’s bounding box can be adjusted within the size of the Default border.
The size of image’s bounding box cannot be adjusted.
· When [Bleed border], [Cropped border], or [Default border] is selected on a canvas on which [Bleed border], [Cropped border], and [Default border] are not set, the size of the [Guide] is adjusted so that it is included in the [Canvas].
(15) Interpolation method
You can select the method for interpolating the colors of pixels when transforming images.
Smooth edges (bilinear)
This method blends the colors of neighboring pixels to create smooth outlines (boundaries between colors). However, outlines may become blurred depending on the image.
When interpolating the image, the pixels in the image are duplicated. Since the colors are not affected by neighboring pixels, outlines (boundaries between colors) remain sharp. However, outlines may become jagged depending on the image.
Clear edges (bicubic)
The average colors of the original pixels are strictly calculated and contained for each pixel after the transformation. Scaling up makes the line sharper and scaling down makes the line smoother. Even detailed lines can be preserved when scaling the image down. However, this method can result in blurred outlines and can take a long time to process depending on the image.











Mesh Transformation [PRO/EX]
1 On the [Layer] palette, select the layer you want to transform.

· Selecting multiple layers transforms all of the selected layers.
· To change the Layer Mask only, you must unlink the Layer and the Layer Mask. For details, see " Link Mask to Layer " .
2 Using a selection tool, create a selection.

If there is no selection area, the entire drawn area of the selected layer will be the target of the transformation.
4 On the [Tool Property] palette, set the number of lattice points (handles).

You can set up to 10 lattice points.
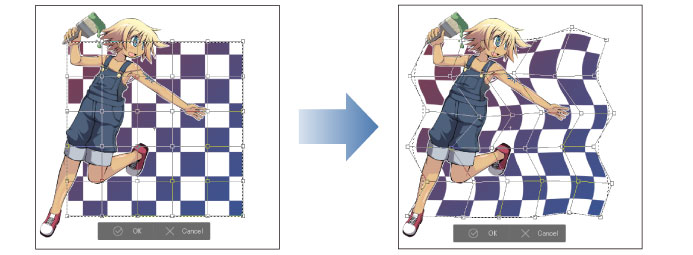
Hold down Shift while dragging a handle to move the handle horizontally, vertically or 45° diagonally.
6 Click [Confirm] on the launcher below the bounding box to apply the transformation.
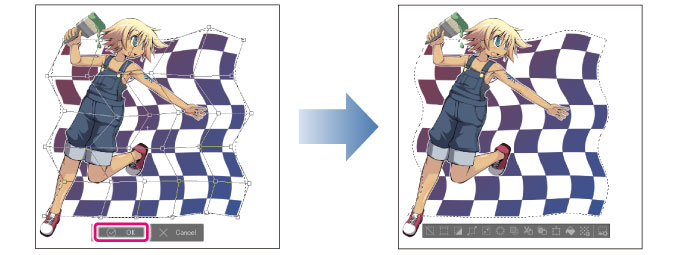
· Double click on areas other than the handles inside the guides to confirm the transformation.
· Pressing Enter also applies the transformation.
· Pressing Esc before confirming the transformation cancels it.
· If the [Transform launcher] does not appear, select [View] > [Object Launcher].
Tool property palette settings
[Mesh Transformation] becomes and item in the [Tool Property] Palette when you are using it.

(1) Reset transformation
Restores the image to the original state before transforming.
(2) Flip horizontal
Flips the image horizontally around the center.
(3) Flip vertical
Flips the image vertically around the center.
Applies the transformation.
(5) Cancel
Cancels the transformation.
(6) Center of rotation
Specifies the center of the image transformation.
You can select from [Center], [Top left], [Top right], [Bottom right], [Bottom left], [Top], [Left], [Right], [Bottom], and [Free position].
(7) Change vector width
If turned on while scaling a vector layer, the line width changes in accordance with the transformation.
(8) Keep original image
When turned on, the original image can be kept when moving or transforming.
(9) Number of horizontal lattice points
Specifies the number of horizontal lattice points.
(10) Number of vertical lattice points
Specifies the number of vertical lattice points.
(11) Interpolation method
Select how the colors of surrounding pixels will blend when the image is transformed.
Each pixel is divided into multiple pixels and calculated as an average of the original pixel colors before transformation. This method makes outlines smoother, but may take a long time to process.
The outline of the color separation borders are blended with the color of the adjacent pixels and smoothed. However, white noise may appear around the outline depending on the content being transformed.











Free Transform
Dragging a handle allows you to transform the image. [Free Transform] allows you to freely transform by dragging a handle.
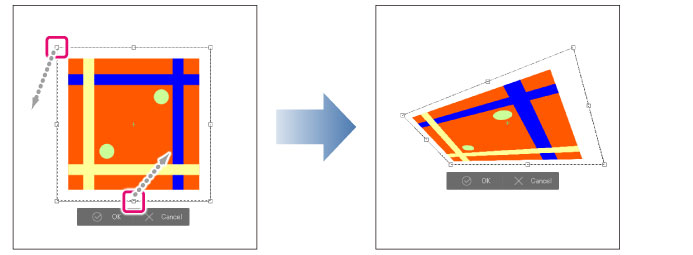
· Hold down Shift while dragging a handle to move the handle according to the direction of the guideline.
· Dragging a handle while holding down Ctrl allows you to scale the image up and down.
· Dragging a handle while holding down Ctrl + Shift allows you to scale the image without changing the original aspect ratio.
· Dragging a handle while holding down Ctrl + Alt keys allows you to scale up/down the image from the center point.
· For details on the Transform operates, see " Transform image " .
· You can also use the [Tool Property] Palette to Transform. For details on the [Tool Property] palette settings, please see to the following " Tool property palette settings " .
· Layers that support [Free Transform] include Raster layers, Vector layers, Layer Masks, Image material layers, Frame Border folders, Rulers, and Selection layers.
Читайте также:

